What Is The Main Goal Of Generative AI? In New 21st Century
A branch of artificial intelligence that is quickly emerging is termed Generative AI. It learns from existing data to create new content. As new forms of technology continue to emerge, AI aims to create high-quality, original works of text, images, music, or intricate designs that express human creativity and problem-solving capabilities. By utilizing advanced technologies which includes neural networks, advanced algorithms to create text or images and even music, and problem-solving AI which is then used for entertainment, art or even new designs in healthcare, background cyber security , automation. It is indeed predicted that AI will help in creativity and efficiency in those aspects at an amazing pace.
Generative AI Objectives
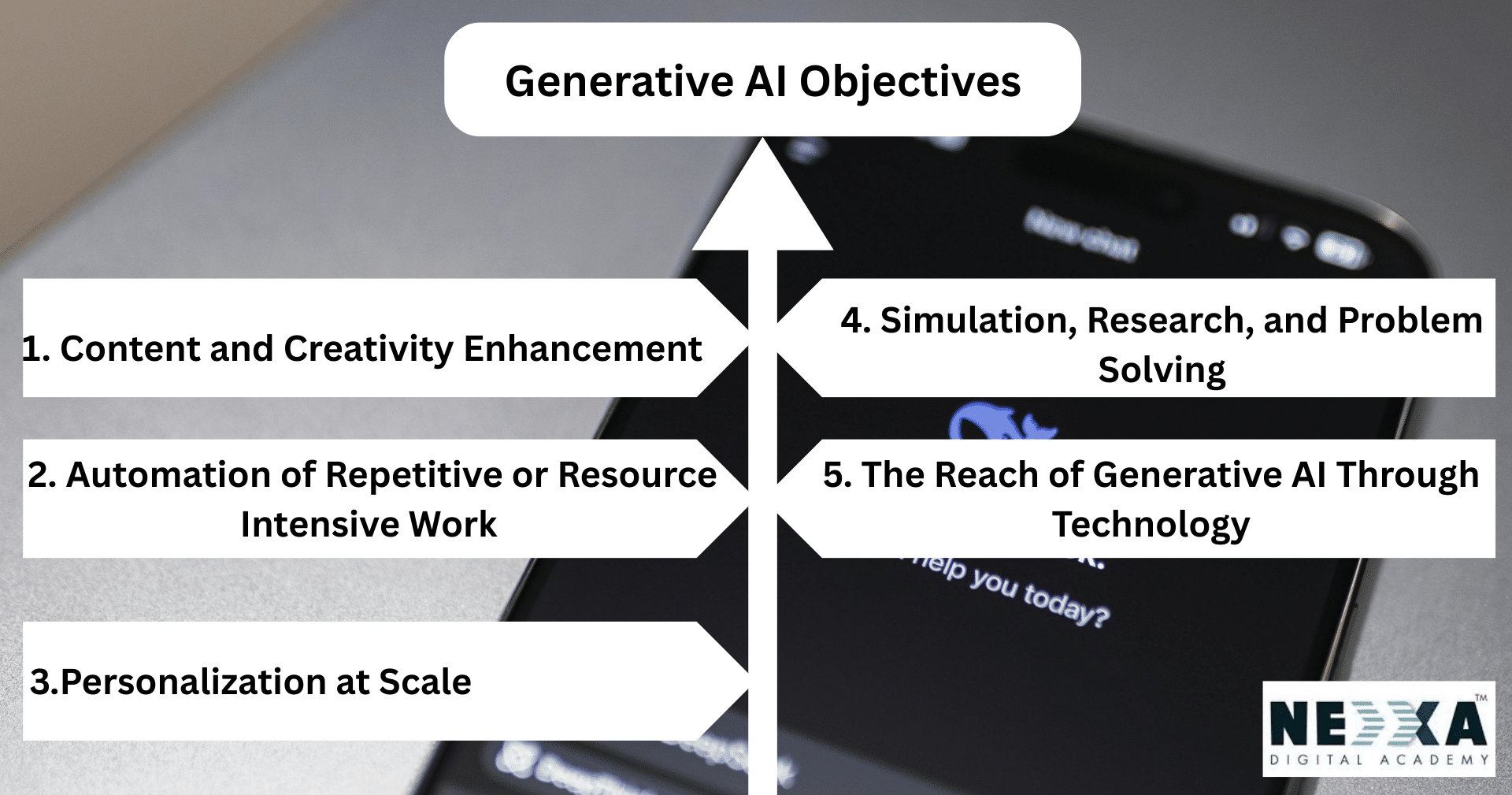
1. Content and Creativity Enhancement
- The efficiency of human creation has been improved due to generative AI. Whether it is writing blog posts, movie scripts, or designing video games or collections of fashion, it is aimed at enhancing human imagination.
- It does not eliminate human creativity, instead it acts as a collaborator to offer suggestions, outlines, and frameworks.
- Example: A writer suffering from a creative block can integrate generative AI to help brainstorm plot ideas. This will reduce time and energy spent.
2. Automation of Repetitive or Resource Intensive Work
- The other automation of systems generative AI aims to complete, within minutes, several content pieces or solutions that would take hours, days or even months to complete.
- Marketers are able to produce ad copies in a span of seconds.
- Architects can produce multiple designs for a given structure.
- Video game developers are able to automatically generate landscapes and characters.
- The automation of such processes allows professionals to use their time and energy on innovative and complex strategies and ideas.
3.Personalization at Scale
- Generative AI has the ability to multi customize a specific product or service to a person. With enough information about a person and how they act, Generative AI is able to create tailored ads, learning content, as well as personalized designs.
- Example: Each user is given a personalised workout plan, diet chart, or lesson plan according to what they require.
4. Simulation, Research, and Problem Solving
- Generative AI remains a critical part of any R&D including cyber security subjects . AI is invented to “foster scientific creativity” by simulating possible outcomes, creating prototypes, and suggesting other solutions.
- In the field of medicine, AI can suggest novel molecular architectures to unlock new drugs.
- In the field of engineering, it can craft new optimal devices.
- In the area of climate change, it can create models to aid in better scenario-building for policy development.
- The focus is to “speed up problem-solving” including cyber security subjects which otherwise would take a huge amount of time and resources.
5. The Reach of Generative AI Through Technology
- There are few people who are not artists, or technically skilled than The people who are not skilled enough to draw, would be able to use artificial tools to generate artwork. The people who do not know how to program or cyber security subjects can be able to produce tangible codes.Thus, the aim of this technology is “to provide everyone the ability to unleash their imagination and invent new ideas”. We should also know what is a key feature of generative AI that helps in enhancing technology.
What Propels Generative AI to Achievement?
We have learned about what is the main goal of generative AI and now In order to understand generative AI outcomes we need to observe the technologies that enable it.
1.Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs):
Relies on the use of text-to-image models, to generate lifelike images, sounds, or audios. They use Generative Adversarial Networks which relies on two analytical neural systems (The generator and the discriminator), for a ‘competitive’ outcome.’’
2.Transformers:
The backbone of large language models (LLMs) such as GPT that are proficient in writing, translating, and summarizing texts.
3.Variational Autoencoders (VAEs):
Used for image generation and data compression process.These models use training data and pattern recognition to create outputs that meet the standards of realism, coherence, and creativity set by humans.
Applications Across Industries
In the real world we have understood what is the main goal of generative AI and what is a key feature of generative AI , such as content creation, personalization, background cyber security provider and problem-solving, are infinite in scope.
1. Entertainment and Media
- Automated generation of screenplays and music.
- Creation of AI characters and worlds for video games.
2. Marketing and Business Industry
- Generated Automated Ad copy
- Personalized Customer Engagement
- AI produces product descriptions to be published.
3. Healthcare
- Producing new drugs and vaccines.
- Generation of synthetic medical data used to train models.
- Suggesting treatment plans tailored to the patient.
4. Education
- Implementing individualized learning approaches for students for their education.
- Supervised self learning materials supplemented by practice assessments and AI managed practical simulation sessions.
- Teachers and AI chatbots provide unlimited additional and individualized asynchronous support along with learning of cyber security subjects for better understanding.
5. Design and Engineering
- Creation of product prototypes at a faster rate.
- Development of architectural plans and blueprints.
- Optimization in industrial designs.
6.Finance
- Generation of reports and predictions on the market.
- Fraud detection and prevention is simulated with the use of synthetic data and background cyber security .
- Tailored reports for each individual offered for their convenience.
How Has Generative AI Affected Security, The Future and The Responsibility

Generative AI captures text, image, video, audio, or even code and produces new content after mastering different datasets. Once has to identify what is a key feature of generative AI in future. Unlike older AI systems that only classified or analyzed data, Generative AI employed Generative Adversarial Networks, VAEs, and large language models like GPT to create entirely new results. The systems’ novel ability to independently create human-like content, however, poses a dilemma in cybersecurity, where the systems’ generative features are both useful and detrimental. One has to learn how has generative AI affected background cyber security and cyber security subjects in the new technology .
In the case of cyber security, a Generative AI is useful in creating realistic attacks to enhance defenses, detect and automate responses to attacks, and controlling proactive attacks where sophisticated malware, phishing, and even deepfake are constructed. There should be a national cyber security policy for a country. The hundreds of thousands of digital marketers in the world should know, for the sake of privacy-first marketing, GDPR compliant marketing, and marketing programmatically in a safe environment, that background cyber security is a core issue. Let’s look at six major things to understand How Has Generative AI Affected background Security and cyber security subjects, with specific focus on both the defense and offense sides.
1. Improvement of Detection of New Security Threats and Associated Procedures
Data breaches can occur from a multitude of sources and can involve ripple effects through multiple systems. Generative AI systems can analyze enormous amounts of datasets to define normal network behavior and track any deviations. Systems AI model behavior and flag system and network access anomalies like traffic jumps, access to unauthorized devices, etc. Tools like Darktrace’s Immune System use machine learning and Generative AI to analyze zero day threats and are able to decrease the time to analyze the 30 percent of data that is the least relevant. As noted in the 2025 background Cyber security Trends, this approach has been proven helpful in reducing the time of analysis to faster levels.
The creation of network models has been greatly advanced through the use of AI systems that generate synthetic data models of network traffic. These models allow the system the ability to ‘zone in’ on subtle repeated behaviors that demonstrate a system that has been set to ignore warning levels below analysts’ set levels. Within the security operations center, AI models concentrate on system behavior and correlate system alerts to threat data and over a bottom to top level interdisciplinary analysis, reprioritize the issue set of the more severe incidents at the top. This interlinking and routing process decreases the number of alerts that are forwarded to the analysts in consequence. This focused approach is called critical system threat focusing.
For example, a bank was able to realize those unusual access to files systems, alerted the AI system and froze the data. The system was saved and the bank managed to save in potential damages, more than 5 million dollars.
An example of how to use it is to implement systems like Splunk and Drive and use systems like Generative AI Tools to overlay signposts in the Datastream.
2. Simulating Attacks to Strengthen Defenses
One of the most transformative applications of AI is its ability to simulate realistic background cyber security attacks, allowing organizations to be proactive in defensive strategies. Generative AI assists background cyber security teams by creating synthetic malware samples or entire attack scenarios used to test systems and train personnel. For example, Generative AI can prepare malware variants or phishing emails to prepare organizations for real-world scenarios.
NVIDIA Morpheus and similar tools harness natural language processing to develop synthetic spear-phishing attacks, achieving 21% greater accuracy in malicious intent modeling than is possible with traditional methods. Such simulations, in tandem with exercises to assess the integration of the ad tech stack and automation of the entire data pipeline, reinforce advanced digital marketing platform defenses.
A tech company, for instance, was able to employ Generative AI to simulate a DDoS attack and, in the process, discovered gaps in its cloud infrastructure which allowed it to mitigate downtime risks by 25%.
Use Generative AI tools to simulate attacks like NVIDIA Morpheus and incorporate actionable real time analytics to proactively identify and patch the gaps.
3. Automating Incident Response and Remediation
Generative AI increases the efficiency of incident response by automating time-consuming processes, including log analysis, threat evaluation, and playbook formulation. AI-based response systems, for example, real time maintenance AI, can decrease response time by isolating affected systems, blocking nefarious traffic, or rolling back compromised systems. For instance, generative AI can create playbooks for specific threat scenarios, with little to no human engagement.
In the sphere of digital marketing, bots that respond autonomously to ad campaigns defend the programmatic ad purchasing layer from ad fraud, thus protecting real-time bidding systems. Virtual security analyst tools, like CrowdStrike’s Charlotte AI, provide real-time analysis and sensitive data scrubs to facilitate compliance with privacy-first marketing. Background cybersecurity teams can focus on higher-level work, increasing productivity by 35%, as monotonous tasks are now automated (source: 2025 SOC trends).
Real World Example: A retail brand that fell victim to a phishing attack was able to block the attack’s traffic by using AI-powered systems, thus protecting the integrity of their marketing campaigns.
Actionable Tips: Employ incident response automation systems like CrowdStrike with AI powered tools for automated defense arm. Ensure data anonymization processes meet GDPR marketing compliance.
4. Attackers with More Advanced Threats – an Updating Autonomy Issue
Unlike in the past, attackers now have in their arsenal the ability to use generative artificial intelligence in attacks such as self evolving malware, sophisticated capable deepfakes, and high intensity personalized spear phishing. With the ability to create sophisticated pivot forging phishing emails in mere seconds, the delay decreases by more than ninety-nine percent and fifty percent. Considering the sophistication of these attacks, traditional systems do not see and analyze them, hence, they become a risk to consent advertising and private first marketing.
Sophisticated systems created by deepfakes have the ability to create audio and video messages impersonating high ranking executives thereby assisting in boss email compromise (BEC) attacks. 85% of security professionals in 2025 believe the increase in deep fakes attacks and cyber attacks in general to generate artificial intelligence. Many believe deep fakes are the fastest growing scams in the online world and there is need for national cyber security policy . Generative artificial intelligence is capable of creating malicious codes that are able to evade the most advanced detection systems. This increases the number of weak points during the integration of the ad tech stack.
For example, during a zoom call, an advanced hacker was able to trick a whole office with a deep fake video of their CEO to claim a large sum of money by bypassing background cyber security arrangements. This proves the advance of generative artificial intelligence and the deep fakes it is capable of.
Conduct campaign that helps the employees to become more aware of the background cyber security attacks spear phished by Artificial intelligence and the Generative stereotypes that work with it. Another way to protect is to use AI systems to locate sophisticated phishing attacks and deepfakes as part of the background cyber security threat detection.
5. Supporting Privacy and Compliance
Privacy-first marketing is possible because Generative AI can generate synthetic data for testing campaigns which does not have real user data. Data anonymization addresses GDPR for marketing and CCPA marketing strategies and reduces privacy risks with national cyber security policy . For example, Synthea and other tools create synthetic datasets that help in testing programmatic ad-buying platforms. These tools also help ensure secure cookie consent management.
Generative AI produces national privacy policy privacy policy and incident response report drafts which reduces legal work and keeps the rest of the organization focused on its core activities. The incident of data leakage, which has been observed in some Large Language Models, is an example of why sensitive data should be governed. It must be known that sensitive data is not to be put in training datasets.
Real-World Example: A marketing agency can be singled out for using Generative AI to create user data for A/B testing which resulted in the proper GDPR marketing and compliance.
Actionable Tip: Generative AI can be used to create synthetic data, for example Synthea. Use cookie consent management tools to ensure privacy-first marketing compliance.
6. Increasing Knowledge and Training in Cyber security
Through the use of Generative AI, unique environments are created where AI can enhance background cyber security training on SOC and marketing personnel. For example, it can reinforce training and retraining on the subject of malware infection attempts and phishing attempts. In Check Point Infinity AI Copilot, it was reported that interactive training Chatbots increased training bounded rationality by 20 percent.
From the marketing angle, background Cyber Security Awareness Month entails the creation of interactive digital content about AI marketing and background Cyber Security. Employees are taught threat identification and escalation as responsible, self-governed and proactive workers by Chatbots powered by NLP.
Example: A machine learning driven phishing simulation training which was aimed at teaching personnel to spot phishing and background cyber security attacks, was able to accomplish a reduction of 30% in the documented cases of phishing attacks to a document at a technology company.
Conclusion: The Goal is Co-Creation
The primary aim of generative AI is not to replace us, but rather to enhance us. It is a product of our imagination—self-defined creativity that has absorbed our imaginative patterns, only to reflect them back at us with more power.
It seeks to become a cocreator throughout the entire human journey of exploration. It wishes to take care of the brute-force computation of possibilities, thus rendering us the liberty to work on the finer details—where the optimal queries are formed, value-based reasoning is employed, and the outputs are layered with significance and essence. We should learn what is key feature of generative AI in future.
In closing, generative AI isn’t aimed at creating content. It is aimed at enhancing human capability. The more appropriate question is not “What can AI do?”, but rather “What are we able to accomplish together now?”
FAQ
1. What is the main goal of generative AI?
The main goal of generative AI is the automated generation of volume. In the case of generative AI applications in digital marketing, this means automating the creation of SEO-optimized blog posts, personalized marketing messages, and advertising images. We should also identify what is a key feature of generative AI in todays world. In all these instances, the model-generated content requires minimal manual intervention and optimizes user engagement. For example, NLG tools like Jasper generate draft blogs that center on keywords such as “SEO for headless CMS,” and AI-assisted advertisement creators help in programmatic advertisement purchases. Marketers have considerably more flexibility in producing AI-assisted content for large volume orders, while human marketers ensure that variable brand elements stay aligned, such as adapting personalized experiences in the moment through real-time AI-optimized voice search and personalized experiences.
2. What is the difference between generative and other types of AI?
Traditional AI is predictive analytics. Predictive analytics is data analysis or data classification. In contrast, generative artificial intelligence is AI that produces content; in other words, it creates text, images, videos, or other items. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and transformer large language models (LLMs) and other AI tools create outputs that exhibit human creativity. We should also identify the key feature of generative AI in the current scenarios.
Artificial intelligence in digital marketing offers blog writing features through generative content theory tools, while traditional AI performs cross-channel attribution to assess marketing campaign effectiveness.
3. How does generative AI enhance SEO strategy formulation?
Automation of certain SEO content time-consuming tasks can be achieved by assessing the AI’s ability to document cluster keywords, which must also focus on creating topic clusters for content authority building. AI can identify clusters of documents through adjacency analysis on a text string, such as between “privacy sandbox marketing” and “SERP feature optimization”. For NLG, automating the creation of blog posts, AI-driven voice search optimized meta descriptions, and FAQs, especially since voice queries are predicted to account for 55% of total queries in 2025. Through automated content gap analysis, AI identifies missed keywords to help maintain ranking comprehensive coverage. Editors still add significant markup to enhance semantic HTML for SEO purposes to improve crawlability and brand voice consistency.
4. Can generative AI comply with privacy laws?
Yes. Generative AI does assist in privacy-first marketing by creating compliant content as alongside with synthetic data. There should be a national cyber security policy . Automated data pseudonymization as part of marketing will assist in compliance with GDPR and CCPA regulations. For example, tools such as Synthea produce synthetic data to conduct programmatic ad buying test campaigns that do not include real user data which diminishes any privacy risks. For users who consent to consent-based advertising, AI-generated ad creatives are used, and cookie consents and cookie management are in place to ensure background cyber security compliance. Human supervision to avoid data leakage remains, and ethical alignment is always implemented. One has to learn what is a key feature of generative AI and how it can help in creating privacy.
5. Will generative AI take the place of marketers?
No. As with all AI tools, ChatGPT is used as an augmentation, not a replacement, to human marketers. While the generative AI content tools do provide ‘support’ in ‘automating’ human ‘ideation’ processes, where automation and hands-off control are available, the strategic value of such tools is limited. AI may produce a blog or an ad copy, and even generate content, but the functions of emotional and cultural recapturing are human and ‘tailoring’ is always a ‘human’ task even in the case of fully automation. Marketers have to learn what is a key feature of generative AI in tech sector. A 2025 study reports that 85% of marketers using AI for ideation, yet 90% of the decision-making is human and there is a need for national cyber security policy . This ensures that campaigns resonate and that brand values are preserved.
